
Video can’t be loaded because JavaScript is disabled: The Legacy of NASA's Kepler Space Telescope: More Planets Than Stars () The Legacy of NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope: More Planets Than Stars. Its data has also helped scientists observe and understand supernovae measurements were collected every half-hour so the light curves were especially useful for studying these types of astronomical events. It was as shut down the same day.ĭuring its over nine and a half years of service, Kepler observed 530,506 stars and detected 2,662 exoplanets. NASA announced its retirement on Octo(the spacecraft ran out of fuel). The Kepler Mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine the fraction of the hundreds of billions of stars in our galaxy that might have such planets. Named after the German astronomer Johannes Kepler (Decem– November 15, 1630), Kepler Space Telescope is a retired space telescope launched by NASA to discover Earth-size planets orbiting other stars – especially those in the habitable zone (also known as the goldilocks zone) of their stars where liquid water might exist on the surface of the planet. Related: NASA’s Planet Patrol Project lets the volunteers help to find exoplanets Kepler Space Telescope Finding exoplanets not only helps humanity to better understand the potential prevalence of life elsewhere in the Universe but also how our Earth and Solar System were formed. The retired Kepler satellite has discovered about half of these first 4000 exoplanets in just one region of the sky, while the new TESS mission is on track to finding even more, all over the sky, orbiting the brightest nearby stars. The faster a planet orbits its parent star, the higher the accompanying tone played. Exoplanets detected by slight jiggles in their parent star’s colors (radial velocity) appear in pink, while those detected by slight dips in their parent star’s brightness (transit) are shown in purple.įurther, those exoplanets imaged directly appear in orange, while those detected by gravitationally magnifying the light of a background star (microlensing) are shown in green. The entire night sky is first shown compressed with the central band of our Milky Way Galaxy making a giant U. The featured video highlights these exoplanets in sound and light, starting chronologically from the first confirmed detection in 1992. Data: NASA Exoplanet Archive.Ĥ,000 exoplanets milestone was passed last month (in June 2019), as recorded by NASA’s Exoplanet Archive. Kepler observed more than a half million stars over the course of its nine years in operation.Video can’t be loaded because JavaScript is disabled: 4000 Exoplanets () 4000 exoplanets. Besides launching us into the golden age of exoplanets, Kepler has reinvigorated the study of stars. The existence of these compact systems raises questions about how solar systems form: Are these planets “born” close to their parent star, or do they form farther out and migrate in? Solar systems are diverse too! While our own inner solar system has four planets, Kepler found systems with considerably more planets - up to eight - orbiting close to their parent stars. The most common size of planet Kepler found doesn’t exist in our solar system - a world between the size of Earth and Neptune - and we have much to learn about these planets.
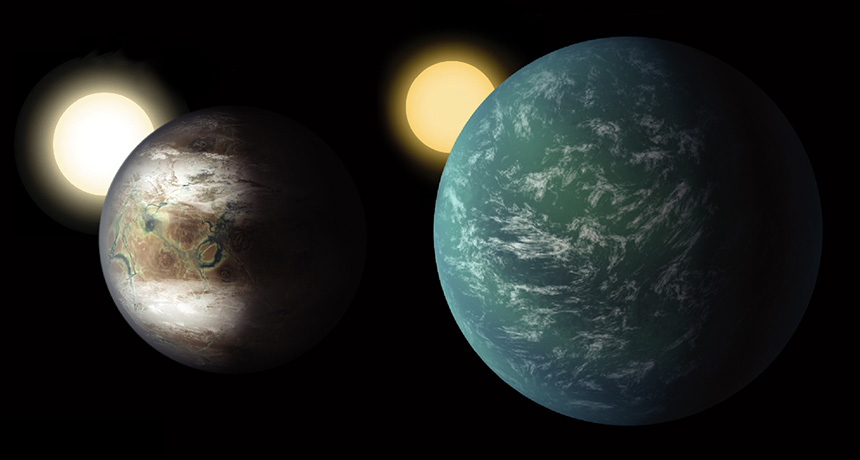
Kepler has discovered a diversity of planet types, opening our eyes to new possibilities. We still have much to learn about whether any of them could host life. Kepler has shown us our galaxy is teeming with terrestrial-size worlds the most recent analysis of Kepler’s discoveries concludes that 20 to 50 percent of the stars in the sky are likely to have small, possibly rocky planets similar in size to Earth within the habitable zone of their parent stars, where water could pool on the planet surface. Kepler has proven there are more planets than stars in our galaxy - and knowing that revolutionizes our scientific understanding of our place in the cosmos.

NASA's Kepler mission revolutionized our scientific understanding of our place in the cosmos by discovering that: The Top Science Results from the Kepler Mission Kepler leaves a legacy of more than 2,600 planet discoveries from outside our solar system, many of which could be promising places for life.
After nine years in deep space collecting data that revealed our night sky to be filled with billions of hidden planets – more planets even than stars – NASA’s Kepler space telescope was retired.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
